Protons neutrons and electrons worksheet – The Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Worksheet provides an engaging and interactive learning experience, empowering students to grasp the fundamental concepts of atomic structure. This worksheet delves into the properties, roles, and significance of protons, neutrons, and electrons, equipping learners with a solid understanding of these subatomic particles.
Through a series of interactive exercises, students will explore the nucleus, electron cloud, and the relationships between atomic number, mass number, and isotopes. This comprehensive resource fosters a deeper understanding of atomic structure and its implications in various scientific fields.
Introduction to Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The fundamental building blocks of atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each particle possesses unique characteristics that determine the properties and behavior of atoms.
Defining Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Protonsare positively charged particles located in the nucleus of an atom. They contribute to the atomic number, which defines the element.
- Neutronsare neutral particles also found in the nucleus. They have no charge and contribute to the mass of an atom.
- Electronsare negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels called electron clouds. They do not contribute significantly to the mass of an atom.
The Structure of an Atom
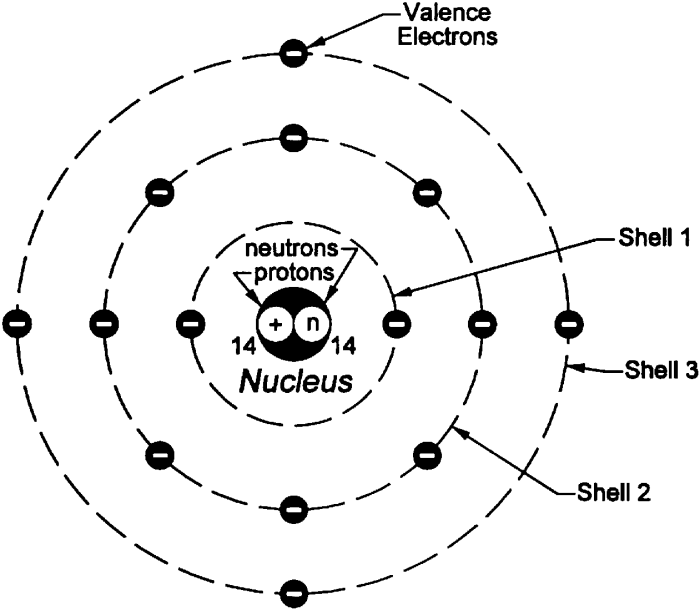
The Nucleus
The nucleus is the central part of an atom, where protons and neutrons reside. It is extremely dense, containing most of the atom’s mass.
The Electron Cloud
Electrons occupy the space surrounding the nucleus in electron clouds. These clouds have specific shapes and orientations, representing the energy levels of the electrons.
Relationship between Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which identifies the element. The number of protons and neutrons together determines the mass number. The number of electrons is typically equal to the number of protons, resulting in a neutral atom.
Atomic Number and Mass Number: Protons Neutrons And Electrons Worksheet

Atomic Number, Protons neutrons and electrons worksheet
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. It uniquely identifies the element and determines its chemical properties.
Mass Number
The mass number of an atom is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. It represents the approximate mass of the atom.
Relationship between Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Element Identity
The atomic number and mass number together define the identity of an element. Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes.
Isotopes
Formation and Properties
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. They have identical chemical properties but differ in physical properties such as mass and radioactivity.
Examples
- Hydrogen has three isotopes: protium (¹H), deuterium (²H), and tritium (³H).
- Carbon has three stable isotopes: carbon-12 (¹²C), carbon-13 (¹³C), and carbon-14 (¹⁴C).
Applications
- Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for imaging and therapy.
- Stable isotopes are used in scientific research to trace elements and study biological processes.
General Inquiries
What are the key features of the Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Worksheet?
The worksheet includes interactive exercises that cover identifying protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom, calculating atomic number and mass number, and working with isotopes.
How does the worksheet help students understand atomic structure?
Through hands-on activities, the worksheet provides a visual and interactive approach to learning about the nucleus, electron cloud, and the relationships between atomic number, mass number, and isotopes.
What are the benefits of using the Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Worksheet in the classroom?
The worksheet enhances student engagement, fosters a deeper understanding of atomic structure, and provides a foundation for further exploration in science and chemistry.