A wet mount requires the addition of certain dyes – A wet mount, an essential technique in microscopy, involves the addition of certain dyes to enhance the visibility and differentiation of specimens. By incorporating specific dyes, researchers can accentuate particular cellular components, facilitate identification, and gain deeper insights into the intricacies of biological samples.
The use of dyes in wet mounts offers several advantages. Dyes can enhance contrast, allowing for clearer visualization of structures and organelles. They can also provide specific information about the chemical composition of cells and tissues, aiding in the identification of different cell types and the detection of specific molecules.
Wet Mounts in Microscopy: A Wet Mount Requires The Addition Of Certain Dyes
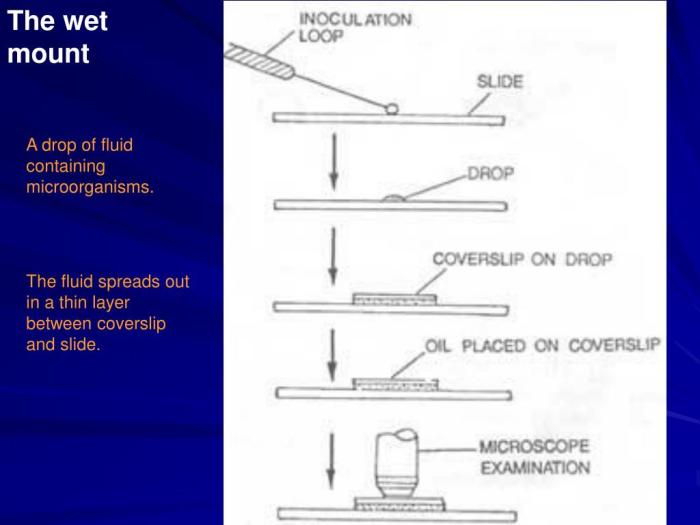
A wet mount is a microscopy preparation in which the specimen is placed on a slide and covered with a drop of liquid, usually water or saline. Wet mounts are used to examine living specimens or specimens that are too delicate to be fixed and stained.
They are also used to examine specimens that are difficult to stain, such as bacteria and viruses.
Wet mounts have several advantages over other microscopy preparations. First, they are simple and quick to prepare. Second, they allow the specimen to be examined in its natural state, without the need for fixation or staining. Third, wet mounts can be used to examine live specimens, which allows the observer to study the specimen’s behavior and movement.
However, wet mounts also have some disadvantages. First, they can be difficult to focus, especially if the specimen is moving. Second, wet mounts can be prone to evaporation, which can cause the specimen to dry out and become damaged. Third, wet mounts can be difficult to store, as the liquid can evaporate and the specimen can become damaged.
Types of Dyes Used in Wet Mounts
There are a variety of different dyes that can be used in wet mounts. The type of dye used will depend on the specimen being examined and the desired results.
- Vital dyesare dyes that can be used to stain living specimens. Vital dyes are typically non-toxic and do not harm the specimen. Examples of vital dyes include methylene blue, neutral red, and acridine orange.
- Non-vital dyesare dyes that can be used to stain dead specimens. Non-vital dyes are typically more toxic than vital dyes and can harm the specimen. Examples of non-vital dyes include hematoxylin, eosin, and safranin.
Methods for Adding Dyes to Wet Mounts
There are two main methods for adding dyes to wet mounts: immersion and staining.
Immersioninvolves placing the specimen in a drop of dye solution. The specimen is then allowed to incubate in the dye solution for a period of time. After incubation, the specimen is washed with water or saline to remove any excess dye.
Staininginvolves applying a drop of dye solution directly to the specimen. The dye solution is then allowed to dry on the specimen. After drying, the specimen is washed with water or saline to remove any excess dye.
When adding dyes to wet mounts, it is important to use the correct concentration of dye. If the dye concentration is too high, the specimen may be damaged. If the dye concentration is too low, the specimen may not be stained properly.
Effects of Dyes on Wet Mounts
Dyes can have a variety of effects on wet mounts. Dyes can change the color of the specimen, making it easier to see. Dyes can also highlight specific structures within the specimen, making them easier to identify. In addition, dyes can be used to kill or immobilize specimens, making them easier to study.
The effects of dyes on wet mounts will depend on the type of dye used, the concentration of the dye, and the length of time that the specimen is exposed to the dye.
Applications of Wet Mounts in Microscopy, A wet mount requires the addition of certain dyes
Wet mounts are used in a variety of applications in microscopy. Wet mounts are commonly used to examine:
- Living specimens, such as bacteria, protozoa, and algae
- Delicate specimens, such as tissue biopsies and cytology specimens
- Specimens that are difficult to stain, such as bacteria and viruses
- Specimens that are being studied for their movement or behavior
Questions and Answers
What are the most commonly used dyes in wet mounts?
Methylene blue, Safranin, and Giemsa stain are among the most frequently used dyes in wet mounts.
How do dyes affect the appearance of specimens in wet mounts?
Dyes interact with specific cellular components, altering their optical properties and making them more visible under the microscope.
What are the factors that influence the staining intensity in wet mounts?
Factors such as dye concentration, incubation time, and pH can influence the intensity of staining.