Unit 8 polygons and quadrilaterals homework 5 rhombi and squares – Embarking on Unit 8: Polygons and Quadrilaterals Homework 5, we delve into the captivating world of rhombi and squares, unraveling their unique properties, classifications, and real-world applications. This exploration promises to illuminate the geometric intricacies of these fascinating shapes, equipping us with a deeper understanding of their significance in various disciplines.
Rhombi, with their alluring symmetry, and squares, as a special case of rhombi, exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from other quadrilaterals. As we delve into their properties, we’ll discover the relationships between their side lengths, angles, and diagonals, unlocking the secrets of their geometric harmony.
Properties of Rhombi and Squares
Rhombi and squares are quadrilaterals with unique properties that set them apart from other shapes. These properties have practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with four equal sides. The opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel, and its opposite angles are congruent. Squares are a special type of rhombus with all four sides and all four angles equal.
Examples of rhombi in the real world include diamonds and playing cards. Squares can be found in objects such as dice, tiles, and picture frames.
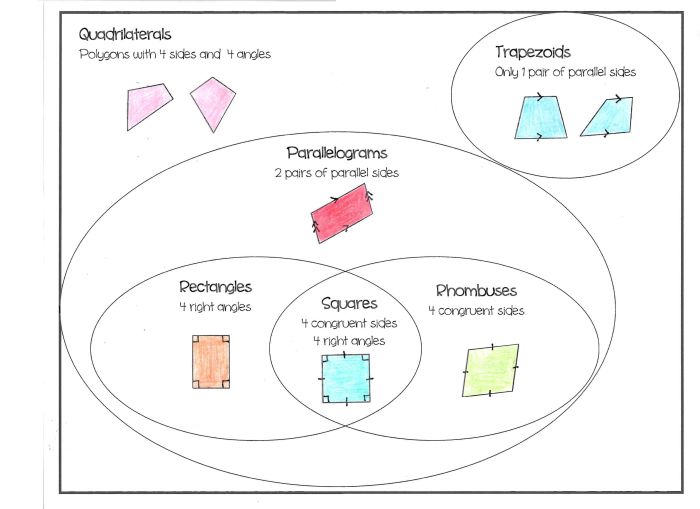
Classification of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals can be classified into different types based on their properties. The following table provides a classification of quadrilaterals based on their side lengths, angle measures, and diagonals:
| Type of Quadrilateral | Side Lengths | Angle Measures | Diagonals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square | All sides equal | All angles are right angles | Diagonals are equal and perpendicular |
| Rectangle | Opposite sides are equal | Opposite angles are equal | Diagonals are equal but not perpendicular |
| Rhombus | All sides are equal | Opposite angles are equal | Diagonals bisect each other at right angles |
| Parallelogram | Opposite sides are parallel | Opposite angles are equal | Diagonals bisect each other |
| Trapezoid | One pair of opposite sides is parallel | Non-parallel sides are not equal | Diagonals are not equal |
Geometric Relationships
There are several geometric relationships between rhombi, squares, and other quadrilaterals. For example, the area of a rhombus is given by the formula A = (1/2) – d1 – d2, where d1 and d2 are the lengths of the diagonals.
The perimeter of a rhombus is given by the formula P = 4s, where s is the length of one side.
The area of a square is given by the formula A = s^2, where s is the length of one side. The perimeter of a square is given by the formula P = 4s.
Applications in Real-World Problems
Rhombi and squares are used in a variety of practical applications. For example, diamonds are used in jewelry because of their hardness and brilliance. Playing cards are made of rhombi because they are easy to shuffle and deal.
Squares are used in architecture to create strong and stable structures. They are also used in engineering to create objects that are resistant to bending and twisting. In design, squares are often used to create a sense of balance and symmetry.
FAQ Section: Unit 8 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Homework 5 Rhombi And Squares
What is the defining characteristic of a rhombus?
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides of equal length.
How are squares different from other rhombi?
Squares are a special type of rhombus with all four angles being right angles.
Can you provide an example of a real-world object that has the shape of a rhombus?
A diamond is an example of a real-world object that has the shape of a rhombus.